

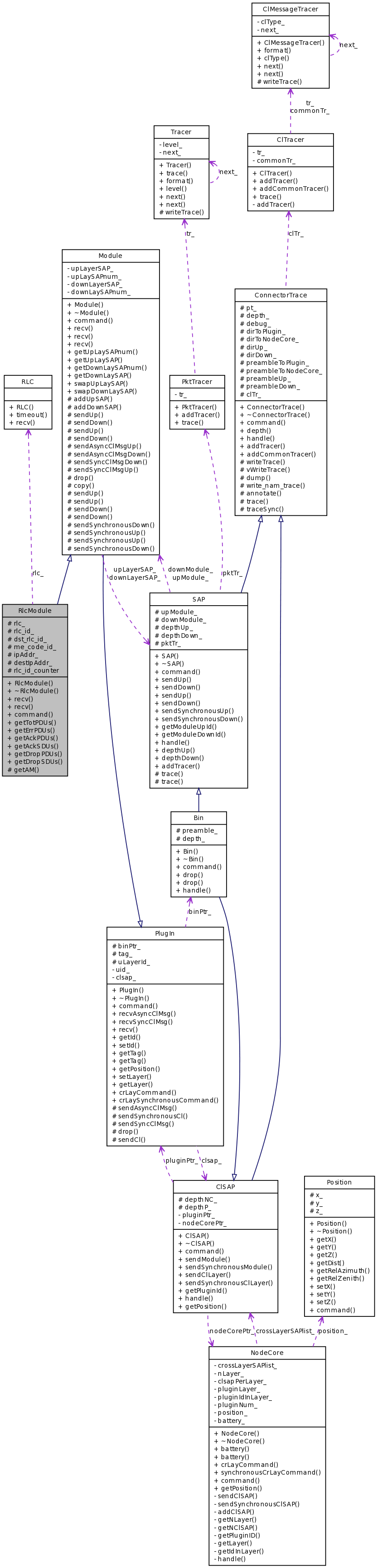
Public Member Functions | |
| RlcModule () | |
| ~RlcModule () | |
| void | recv (Packet *p) |
| void | recv (Packet *p, Handler *callback) |
| int | command (int argc, const char *const *argv) |
| virtual int | getTotPDUs () |
| virtual int | getErrPDUs () |
| virtual int | getAckPDUs () |
| virtual int | getAckSDUs () |
| virtual int | getDropPDUs () |
| virtual int | getDropSDUs () |
Protected Member Functions | |
| AM * | getAM () |
Protected Attributes | |
| RLC * | rlc_ |
| int | rlc_id_ |
| int | dst_rlc_id_ |
| unique identifier of each RLC instance | |
| int | me_code_id_ |
| static counter for id generation | |
| int | ipAddr_ |
| safely returns a pointer to the AM RLC | |
| int | destIpAddr_ |
Static Protected Attributes | |
| static int | rlc_id_counter = 0 |
Definition at line 41 of file rlc-module.h.
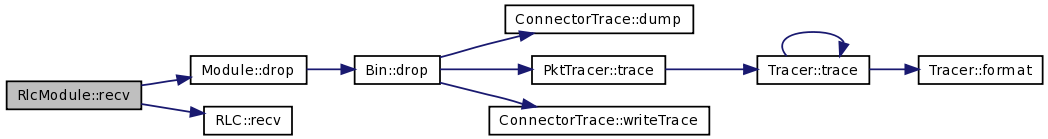
| void RlcModule::recv | ( | Packet * | p | ) | [virtual] |
Abstract method which has to be filled with the ad-hoc operations that the module has to do to the packet received
| p | pointer to the packet will be received |
Implements Module.
Definition at line 124 of file rlc-module.cc.
References destIpAddr_, DOWN, Module::drop(), hdr_rlc::dst_rlc_id_, RLC::recv(), rlc_, rlc_id_, and UP.
Here is the call graph for this function:
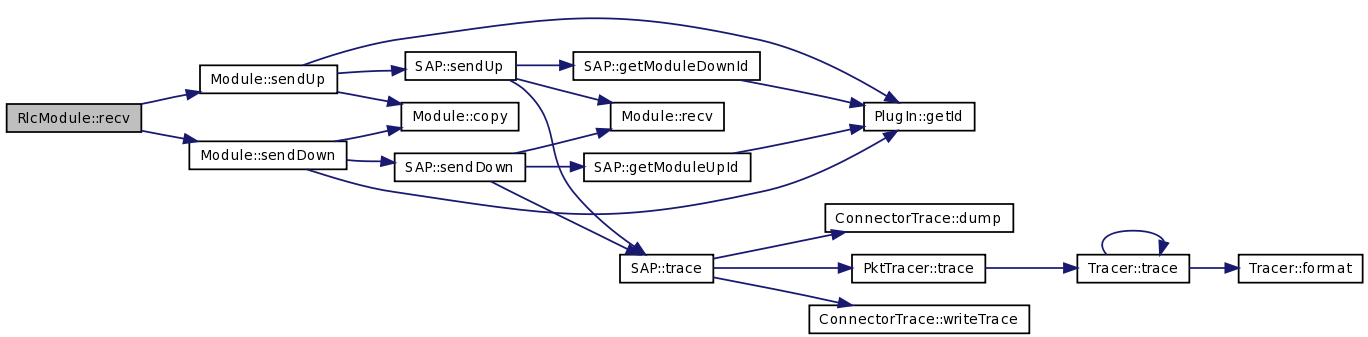
| void RlcModule::recv | ( | Packet * | p, | |
| Handler * | callback | |||
| ) | [virtual] |
This method is called by RLC::sendUp() and Rlc::sendDown() since eurane RLC sees RlcModule as being as being both its down-target and up-target. RlcModule then forwards the packet to upper and lower modules using Miracle methods Module::sendUp(p) and Module::sendDown(p)
| p | pointer to the packet | |
| callback | unused, kept only for compatibility |
Reimplemented from Module.
Definition at line 195 of file rlc-module.cc.
References hdr_umtsphy::data, DOWN, hdr_rlc::dst_rlc_id_, dst_rlc_id_, hdr_umtsphy::me_code_id, me_code_id_, rlc_id_, Module::sendDown(), Module::sendUp(), hdr_rlc::src_rlc_id_, and UP.
Here is the call graph for this function:
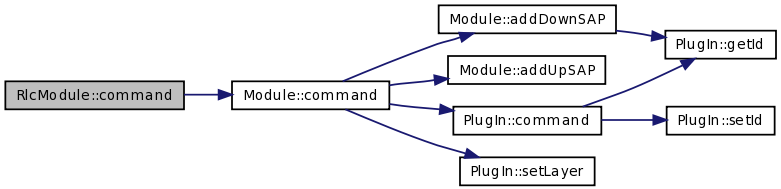
| int RlcModule::command | ( | int | argc, | |
| const char *const * | argv | |||
| ) | [virtual] |
TCL command interpreter. It implements the following OTcl methods:
Moreover it inherits all the OTcl method of PlugIn
| argc | number of arguments in argv | |
| argv | array of strings which are the comand parameters (Note that argv[0] is the name of the object) |
Reimplemented from Module.
Definition at line 62 of file rlc-module.cc.
References Module::command(), dst_rlc_id_, me_code_id_, rlc_, rlc_id_, and rlc_id_counter.
Here is the call graph for this function:
| AM * RlcModule::getAM | ( | ) | [protected] |
corresponding to dst_rlc_id. Note that it is used only in the core network to determine which is the destination. It is not de facto used at Mobile Equipments since all base station attempt to receive all incoming transmissions anyway.
Definition at line 224 of file rlc-module.cc.
References rlc_.
Referenced by getAckPDUs(), getAckSDUs(), getDropPDUs(), getDropSDUs(), getErrPDUs(), and getTotPDUs().
int RlcModule::rlc_id_counter = 0 [static, protected] |
the id of the other RLC instance connected with this one
Definition at line 63 of file rlc-module.h.
Referenced by command(), and RlcModule().
 1.5.2
1.5.2